Low Endorphins and Addiction (And Why Relief Becomes Compulsion): How to Restore Natural Relief
Addiction is often framed as a problem of bad choices, weak discipline, or flawed character.
But for many people, addiction has a far quieter — and far more biological — origin:
👉 A nervous system that cannot generate enough natural relief.
At the center of this issue is a class of neurochemicals that rarely get discussed strategically in recovery:
🧠 Endorphins — the body’s internal painkillers, stress buffers, and emotional stabilizers.
When endorphin levels are low, life feels sharper, heavier, and harder to tolerate. Emotional pain lingers longer. Physical discomfort feels louder. Stress cuts deeper. Pleasure feels distant or unreliable.
And when relief is scarce, the nervous system will hunt for it.
This article explores the low-endorphin–addiction relationship, how it forms, why it becomes self-reinforcing, and how to restore endorphin balance naturally as part of long-term addiction recovery and nervous system healing.
By the end, you’ll understand not only what endorphins are — but how to optimize them without replacing one dependency with another.

What Are Endorphins? 🧠✨
Endorphins are endogenous (internally produced) opioid peptides.
In simple terms:
Endorphins are the body’s built-in pain relief and emotional buffering system.
Endorphins: What They Do (and When They Release)
Endorphins act like your internal relief system — buffering pain and stress, and helping you return to baseline after strain.
Their primary functions include:
- Reducing physical pain
- Buffering emotional distress
- Creating feelings of relief and safety
- Supporting resilience under stress
- Promoting calm pleasure and satisfaction
- Helping the body return to baseline after strain
Endorphins are released during experiences that signal:
- Survival
- Bonding
- Accomplishment
- Movement
- Rhythm
- Relief
When endorphins are healthy, people often experience:
- Emotional durability
- Higher pain tolerance
- Stress that passes instead of accumulating
- A sense of internal reward after effort
- Less urgency to escape discomfort
Endorphins don’t create euphoria — they create tolerability.
They make life feel manageable.
What Happens When Endorphins Are Low? ⚠️
Low endorphin signaling creates a state of pain sensitivity and emotional fragility.
Common signs include:
- Heightened emotional pain
- Low stress tolerance
- Chronic aches or bodily discomfort
- Feeling easily overwhelmed
- Difficulty experiencing pleasure or reward
- Strong craving for relief-based behaviors
- A sense that life feels “too intense”
Many people with low endorphins don’t feel anxious in the classic sense.
Instead, they feel raw.
Life touches the nervous system too directly — without cushioning.
This is fertile ground for addiction.

The Low-Endorphin–Addiction Loop 🔁
Endorphin deficiency and addiction form a closed feedback loop.
There are two main entry points.
1 Low Endorphins → Substance or Behavior Use
Some people begin life with lower baseline endorphin activity due to:
- Genetics
- Early trauma or chronic stress
- Pain conditions or illness
- Repeated emotional suppression
- Lack of physical play or movement
These individuals often discover — consciously or unconsciously — that certain substances or behaviors provide instant relief.
Common endorphin-boosting escapes include:
The nervous system learns quickly:
This is what relief feels like.
2 Substance or Behavior Use → Lower Endorphins
Others begin using substances or behaviors without prior endorphin issues.
But repeated external stimulation causes the brain to adapt by:
- Reducing endogenous endorphin production
- Down-regulating opioid receptors
- Increasing pain sensitivity at baseline
Over time, natural relief becomes inaccessible without the behavior.
The nervous system is no longer generating comfort — it’s outsourcing it.

Why Opioids Feel Like “Home” — Then Become a Trap 💊
Opioids bind directly to the brain’s opioid receptors — the same receptors endorphins use.
Initially, this produces:
- Deep emotional relief
- Pain elimination
- A sense of safety and warmth
- Nervous system quieting
But the brain adapts.
To protect itself, it responds by:
- Reducing natural endorphin production
- Decreasing receptor sensitivity
- Increasing baseline pain and distress
Eventually:
- Relief disappears
- Pain increases
- Withdrawal amplifies suffering
The substance doesn’t just stop working —
it creates the pain it once relieved.
This is not a failure of will.
It is predictable neurobiology.
Alcohol, Endorphins, and Emotional Numbing 🍷
Alcohol indirectly increases endorphin release while also activating GABA.
This combination produces:
But chronic alcohol use:
Many people don’t drink to feel good —
they drink to feel less.
That’s an endorphin story.
Over-Exercise & Over-Tanning: The “Healthy” Addictions ☀️🏃
Endorphins are released during:
- Intense physical exertion
- Pain + effort thresholds
- UV exposure
For some nervous systems, these become primary coping tools.
Signs of endorphin-driven overuse include:
These behaviors aren’t inherently bad — but when they become the only source of relief, imbalance forms.
The goal is restoration, not suppression.

Root Causes of Endorphin Deficiency 🌱
Low endorphins rarely occur alone.
Common contributors include:
- Chronic stress or unresolved trauma
- Long-term opioid or alcohol exposure
- Inflammation and gut dysfunction
- Sleep disruption
- Lack of safe physical touch or connection
- Emotional suppression
- Sedentary lifestyles or extreme overtraining
Do Endorphin Supplements Exist? 🤔
(Yes — But Only in a Very Specific Way)
Endorphins themselves cannot be supplemented directly.
They are large peptide molecules made inside the body — not something you can swallow and absorb intact.
However…
👉 Endorphin levels can be increased indirectly by either
- stimulating their production, or
- preventing their breakdown.
This distinction matters — especially in addiction recovery.
Below are the two most relevant supplements in this category, along with clear guidance on who they’re for (and who they’re not for).
1️⃣ DLPA (DL-Phenylalanine): Dopamine + Endorphin Synergy ⚡
- L-Phenylalanine (LPA) → boosts dopamine (which can convert downstream into norepinephrine and epinephrine)
- D-Phenylalanine (DPA) → increases endorphins by slowing their breakdown
- Motivation + reward (dopamine)
- Relief + pain buffering (endorphins)
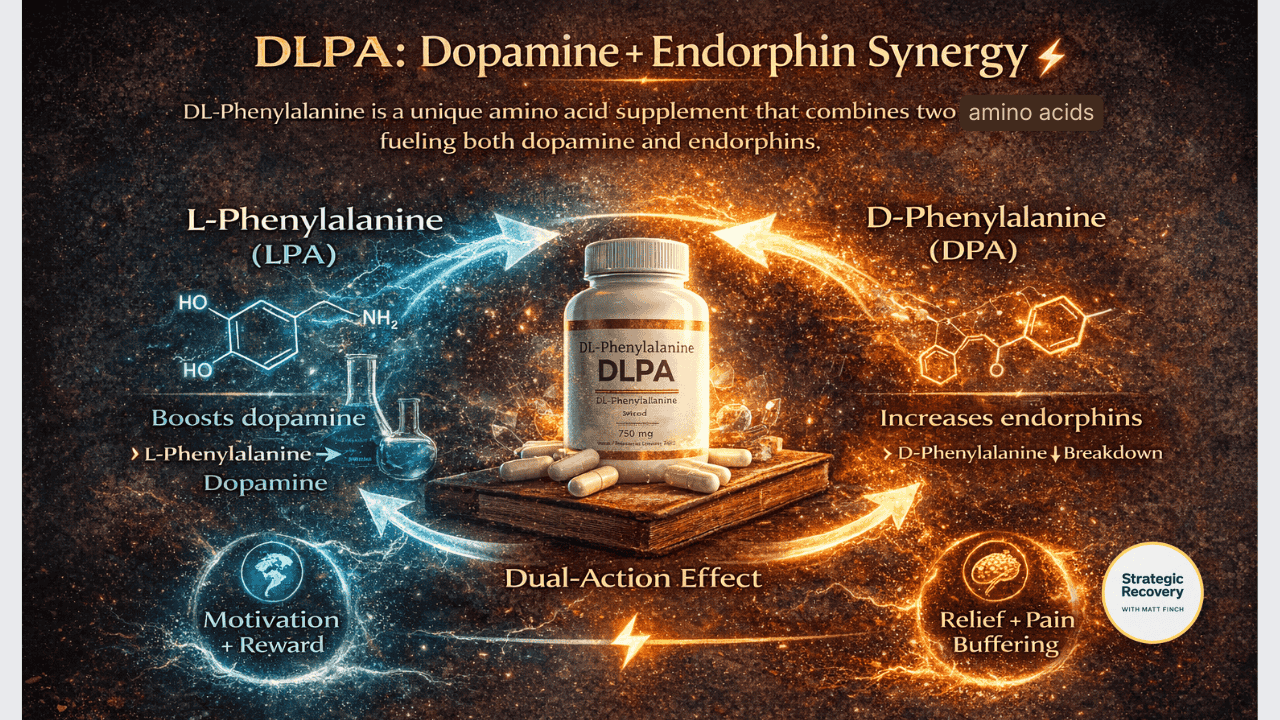
Why DLPA Can Feel Powerful
- Increase the intensity of endorphin-mediated relief
- Prolong the duration of natural pain relief and well-being
- Reduced emotional pain
- Improved mood
- Less craving for external relief
- Greater resilience under stress
⚠️ IMPORTANT CAUTION: DLPA Is Not for Everyone
Approximately 1 in 10 people do not tolerate DLPA well.
Why?
Because the L-phenylalanine component increases catecholamines, which can overstimulate certain nervous systems.
Potential side effects (in susceptible individuals):
- Elevated blood pressure
- Agitation or irritability
- Anxiety or panic
- Hyperarousal or anger
- Impatience or restlessness
- Insomnia
- Headaches
Too activating to be worth it.
2️⃣ DPA (D-Phenylalanine): Pure Endorphin Support 🧬
D-Phenylalanine (DPA) is the clean alternative.
Unlike DLPA, DPA does NOT boost dopamine.
How DPA Works (The “Pac-Man” Effect)
DPA increases endorphins by inhibiting the enzymes that break them down, including:
- Carboxypeptidase A
- Enkephalinase
- Other endorphin-degrading enzymes
-
DPA blocks the Pac-Man enzymes that normally chew up your endorphins
-
Endorphins last longer
-
Net endorphin levels rise
-
Relief increases without stimulation
This allows a natural surplus of endorphins to circulate where the body needs them most.

Why DPA Is Ideal for Sensitive Nervous Systems
DPA is especially well-suited for people who:
- Get anxious or overstimulated easily
- Have high blood pressure concerns
- Are sensitive to dopamine or stimulants
- Are early in recovery
- Experience emotional or physical pain without motivation deficits
- Increases endorphins without activation
- No dopamine surge
- No stimulant-like effects
- Typically no risk of anxiety or agitation
The trade-off?
You don’t get the dopamine/endorphin synergy — only endorphin support.
For many people in recovery, that’s actually a feature, not a flaw.
Availability & Quality Notes 🧪
DPA is a rare and underutilized supplement.
Only a small number of companies manufacture it due to its fully synthetic, specialized nature.
- Montiff Pure D-Phenyl Relief is the best product on the market (500 mg D-phenylalanine capsules)
- Other versions exist through a few specialty supplement manufacturers, but availability is limited and changes frequently
- Start low
- Observe your response
- Prioritize nervous system stability over intensity

🧬 DLPA vs DPA: Endorphin Support Compared
Both support endorphins — but they feel very different in the body. The key is matching the supplement to your nervous system: stability over intensity.
| Feature | DLPA (DL-Phenylalanine) | DPA (D-Phenylalanine) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Action | Increases dopamine and endorphins | Increases endorphins only |
| Mechanism | LPA → dopamine synthesis | DPA → slows endorphin breakdown | Inhibits endorphin-degrading enzymes (enkephalinase, carboxypeptidase A, others) |
| Effect Profile | Motivating + relieving | Relieving + stabilizing |
| Endorphin Effect | ✔️ Yes | ✔️ Yes |
| Dopamine Effect | ✔️ Yes | ❌ No |
| Stimulation Level | Moderate → High (for some) | Very Low |
| Risk of Overactivation | ⚠️ Possible (~1 in 10) | ✅ Minimal |
| Common Side Effects (Susceptible Users) |
Anxiety, agitation, insomnia, anger, elevated BP, headache | Rare |
| Pain Relief Support | Strong (opioid potentiation) | Moderate–Strong (via preservation) |
| Best For | Low motivation + low pleasure + low endorphins | Emotional/physical pain + nervous system sensitivity |
| Not Ideal For | Anxiety-prone, hypertensive, hyperaroused individuals | Those needing dopamine/motivation support |
| Recovery Phase Fit | Mid- to late-stage recovery (with caution) | Early or sensitive-stage recovery |
| Dependency Risk | Low when used correctly | Very low |
| Overall Nervous System Impact | Can feel activating | Calming, buffering, grounding |
Who Should Use Which?
Use this as a quick matching guide — the goal is nervous system fit: stability when you need it, gentle motivation when you can handle it.
Consider DLPA if you:
Motivation + Relief- Feel emotionally flat and unmotivated
- Struggle with low drive, low reward, or anhedonia
- Do not have significant anxiety or blood-pressure issues
- Tolerate stimulatory supplements well
- Are in stable recovery and seeking gentle motivation + relief
Consider DPA if you:
Relief without activation- Feel emotionally or physically raw
- Are sensitive to stimulation
- Have anxiety, panic, or hyperarousal tendencies
- Have had side effects from DLPA or dopaminergic supplements
- Are in early recovery or prioritizing nervous system stability
- Want relief without activation
Key Strategic Recovery™ Principle:
If a supplement increases relief but also increases agitation, it’s not the right tool — no matter how “effective” it looks on paper.
- Endorphins cannot be swallowed — but they can be preserved
- DLPA = dopamine + endorphin synergy (powerful, but not universally tolerated)
- DPA = pure endorphin support (calm, stable, low-risk)
- Sensitivity is information, not weakness
- Relief should stabilize the nervous system — not overstimulate it
In Strategic Recovery™, the goal is not chasing intensity.
It’s restoring internal relief capacity — safely, sustainably, and without creating a new dependency.

Natural Ways to Increase Endorphins 🌿
Restoring Relief Without Creating Dependency
Endorphins are released when the nervous system receives clear signals of safety, rhythm, effort, connection, and meaning.
The goal is not intensity —
it’s consistent, embodied relief.
Below are the most reliable, non-addictive ways to restore endorphin signaling.
1 Rhythmic Movement (Especially Outdoors) 🚶♂️☀️
Endorphins are strongly tied to rhythm and repetition.
- Walking
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Light jogging
- Moderate resistance training
Outdoor movement in natural sunlight can boost endorphins at least twice as much as indoor exercise due to combined physical exertion, sunlight exposure, visual depth, and circadian alignment.
Consistency matters more than intensity.
The nervous system rewards returning, not pushing.

Sunlight & Nature Exposure (Without Compulsion) ☀️🌲
Moderate sunlight stimulates:
- Endorphin release
- Vitamin D production
- Opioid receptor signaling
Helpful practices include:
- Morning or midday light exposure
- Gentle sun on skin
- Time in green or natural environments
⚠️ The key distinction is exposure vs. compulsion.
Sunlight supports endorphins when it’s restorative — not obsessive.

Music, Rhythm & Collective Movement 🥁🎶
The nervous system responds profoundly to rhythm.
Endorphin-rich practices include:
- Music with emotional resonance
- Singing or chanting
- Drumming
- Rhythmic breathing
Group chanting, spiritual singing, and communal dance are especially powerful because they combine:
- Rhythm
- Breath
- Synchrony
- Meaning
- Social bonding
This is why religious ceremonies, tribal dances, and spiritual gatherings have regulated nervous systems for thousands of years.

Temperature Contrast (Brief, Not Extreme) ❄️🔥
Short, controlled stressors (“Hormesis”) trigger an endorphin rebound.
- Cold showers
- Cold exposure (brief)
- Sauna (when appropriate)
- Voluntary
- Time-limited
- Followed by rest
Chronic or extreme stress suppresses endorphins.
Brief contrast restores them.

Foods That Support Endorphins 🍫🌶️
Certain foods reliably stimulate endorphin release through taste, sensation, and biochemistry.
- Contains compounds that stimulate endorphins
- Also supports dopamine and mood
- Most effective in moderate, intentional use
- Trigger mild pain → endorphin rebound
- The body releases endorphins to counteract the heat
- Endorphins are peptides — amino acids matter
- Improve gut-brain signaling
- Support neurotransmitter balance overall
Relief works best when it’s rhythmic, not compulsive.
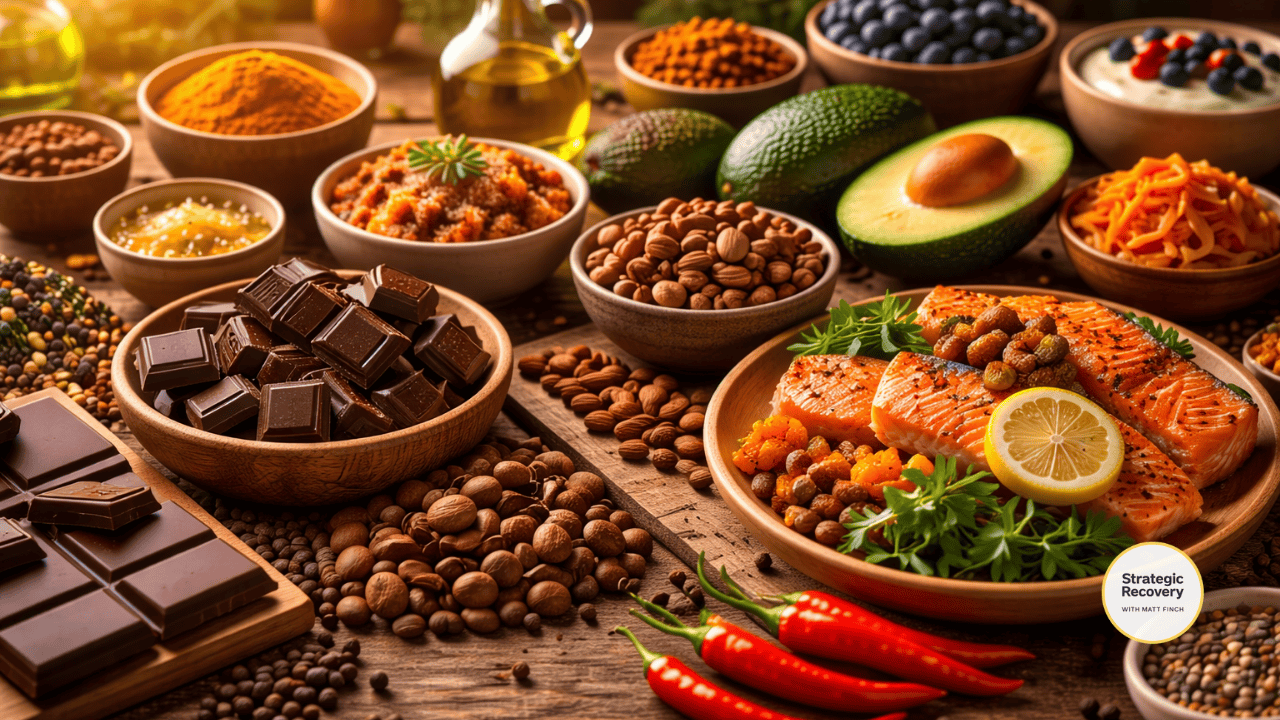

Nutrients That Support Endorphin Health 💊
While endorphins can’t be supplemented directly, the body needs the right building blocks and environment to produce them.
- Adequate protein & amino acids (endorphins are peptides)
- Omega-3 fatty acids (support opioid receptor health)
- Magnesium (reduces pain signaling and stress load)
- Vitamin D (linked to opioid receptor function and mood)
- Zinc (supports neuropeptide synthesis)
Chronic under-eating, extreme dieting, or nutrient depletion can suppress endorphins and increase craving vulnerability.
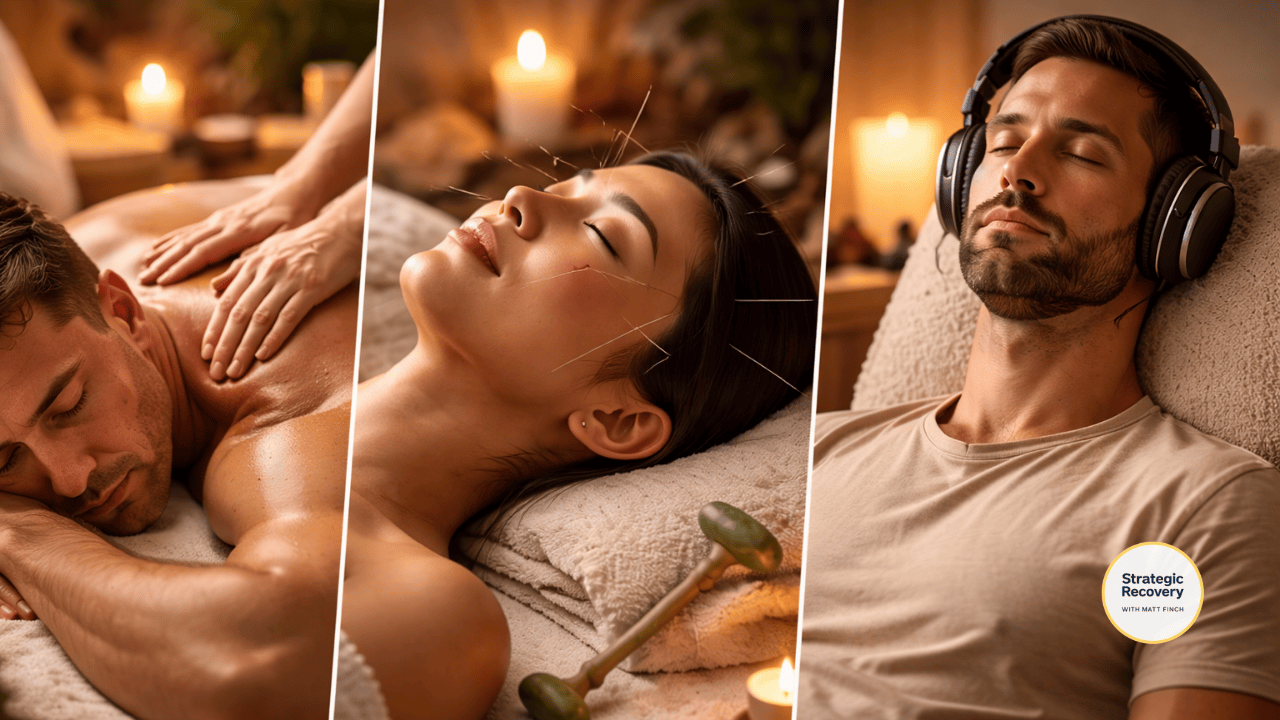
Advanced Endorphin Supports
If you want a powerful endorphin boost without creating a new dependency, these “whole-system” modalities can be game-changers — especially when you use them with stability over intensity.
7.1 — Massage Therapy (especially deep tissue work)
7.2 — Acupuncture + AcuDetox
7.3 — Frequencies & Brainwave Entrainment
7.4 — Safe Intimacy & Connection

🧬 The Strategic Recovery™ Endorphin Optimization Protocol
A Simple Protocol for Restoring Relief Without Replacing One Dependency With Another
Endorphin healing is not about chasing pleasure or intensity.
It’s about retraining the nervous system to generate relief internally again — reliably, gently, and without external crutches.
This protocol is progressive, not rigid.
Move through the phases at your own pace.
🧠✨ 5-Phase Endorphin Restoration
Restore internal relief capacity — safely, sustainably, and without creating a new dependency.
1 Stabilize First (Remove Artificial Relief)
2 Restore Rhythm (Daily, Predictable Inputs)
3 Support the Substrate (Biochemistry)
4 Meaning + Connection (Emotional Buffering)
5 Gentle Contrast (Optional)
Strategic Recovery™ Reminder
Endorphins return when the nervous system learns that relief is available without escape.
Instead of forcing happiness…

Low-Endorphin Self-Assessment
Answer yes or no to the following:
Key Takeaways 🔑
Here’s the big picture — distilled into practical, recovery-relevant truths.
Endorphins are the body’s natural pain-relief system — your built-in “natural morphine.”
Low endorphins increase addiction vulnerability by amplifying pain sensitivity, emotional rawness, and craving urgency.
Opioids, alcohol, over-exercise, and tanning can replace missing relief when the internal system is depleted.
External relief suppresses internal production over time — the nervous system adapts by outsourcing comfort.
Endorphins can be restored naturally through rhythm, connection, nutrition, sunlight (in moderation), and movement.
Relief doesn’t have to be addictive to be real — it can be safe, repeatable, and sustainable.
Your nervous system isn’t defective — it’s responding exactly as biology predicts under chronic stress.
It’s been starved of relief — and relief can be rebuilt without chains attached.
Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only and is not medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, especially if you have existing medical conditions or take prescription medications.




Leave a Reply